How to operate a drone? This seemingly simple question opens a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to efficient surveying and inspection. Mastering drone operation, however, requires a blend of technical skill, safety awareness, and a deep understanding of relevant regulations. This guide will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to navigate the skies responsibly, capturing stunning visuals and experiencing the thrill of flight firsthand.
We’ll cover everything from pre-flight checks and essential controls to advanced flight modes and post-flight maintenance, ensuring a smooth and enjoyable drone experience.
This comprehensive guide provides a step-by-step approach to learning how to operate a drone, covering pre-flight checks, flight controls, advanced features, photography techniques, post-flight procedures, troubleshooting, legal considerations, and battery safety. We aim to equip you with the knowledge and skills to fly a drone safely and effectively.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting various components and adhering to safety regulations. Failing to do so can lead to accidents or malfunctions.
Drone Pre-Flight Inspection, How to operate a drone

A comprehensive pre-flight inspection should be performed before every flight. This helps identify potential issues and prevents accidents.
| Component | Check | Acceptable Condition | Unacceptable Condition & Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Inspect for damage, cracks, or warping. | No damage, firmly attached. | Damaged propellers should be replaced. |
| Battery | Check battery level and condition. | Sufficient charge, no visible damage. | Charge battery or replace if damaged. |
| Gimbal | Check for smooth movement and proper function. | Smooth, unobstructed movement. | Check for obstructions or recalibrate if necessary. |
| GPS Signal | Confirm a strong GPS signal. | At least 8 satellites acquired. | Relocate to an area with better GPS reception. |
| Camera | Check camera lens for clarity and obstructions. | Clean lens, no obstructions. | Clean the lens if necessary. |
| Airframe | Inspect for any damage or loose parts. | No visible damage, all parts securely fastened. | Repair or replace damaged parts. |
| Remote Controller | Ensure sufficient battery power and proper connection. | Sufficient battery, strong connection. | Charge the remote controller or check the connection. |
Safety Regulations and Best Practices
Responsible drone operation requires adherence to both local and national regulations. Understanding and implementing these regulations is critical for preventing accidents and maintaining public safety.
- Always maintain visual line of sight with your drone.
- Never fly near airports or other restricted airspace.
- Respect people’s privacy and avoid flying over private property without permission.
- Fly responsibly and avoid endangering others.
- Be aware of local weather conditions and avoid flying in adverse weather.
- Register your drone with the relevant authorities (where applicable).
Safe Drone Launch and Flight Decision-Making Flowchart
A flowchart helps visualize the decision-making process for a safe drone launch and flight, ensuring all necessary checks are completed before takeoff.
The flowchart would begin with a check for sufficient battery power, followed by a GPS signal check, then an assessment of weather conditions, and finally, confirmation of clear airspace. If any of these checks fail, the launch would be aborted. If all checks pass, the drone would be launched and monitored throughout the flight. In case of any issues during the flight, the flowchart would guide the operator through safe landing procedures, including the use of the Return-to-Home (RTH) function if available.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning to safely and effectively handle your drone is crucial, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone. This site provides comprehensive guidance on everything from basic maneuvers to more advanced techniques, ensuring you’re prepared for a successful flight.
Proper drone operation ultimately ensures both safety and optimal performance.
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation

Understanding your drone’s controls is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section covers the basic controls and calibration procedures.
Drone Remote Control Functions
Typical drone remotes have two control sticks and several buttons. Each element serves a specific function.
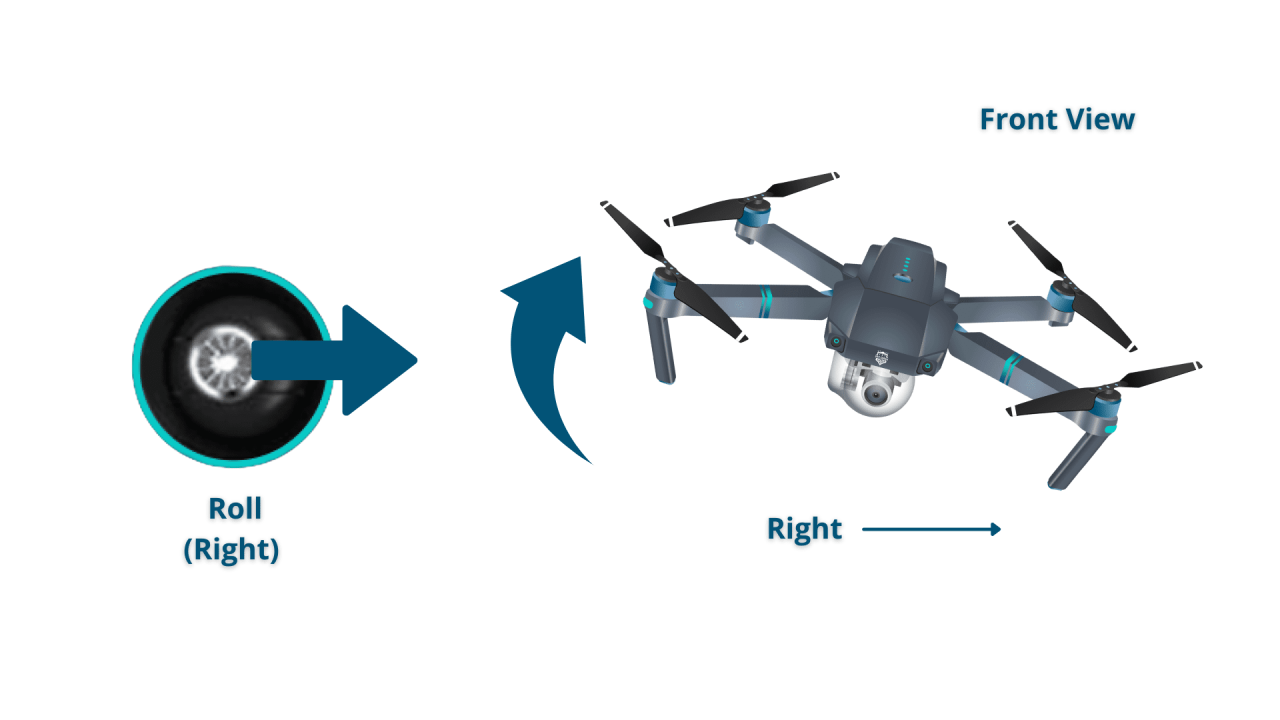
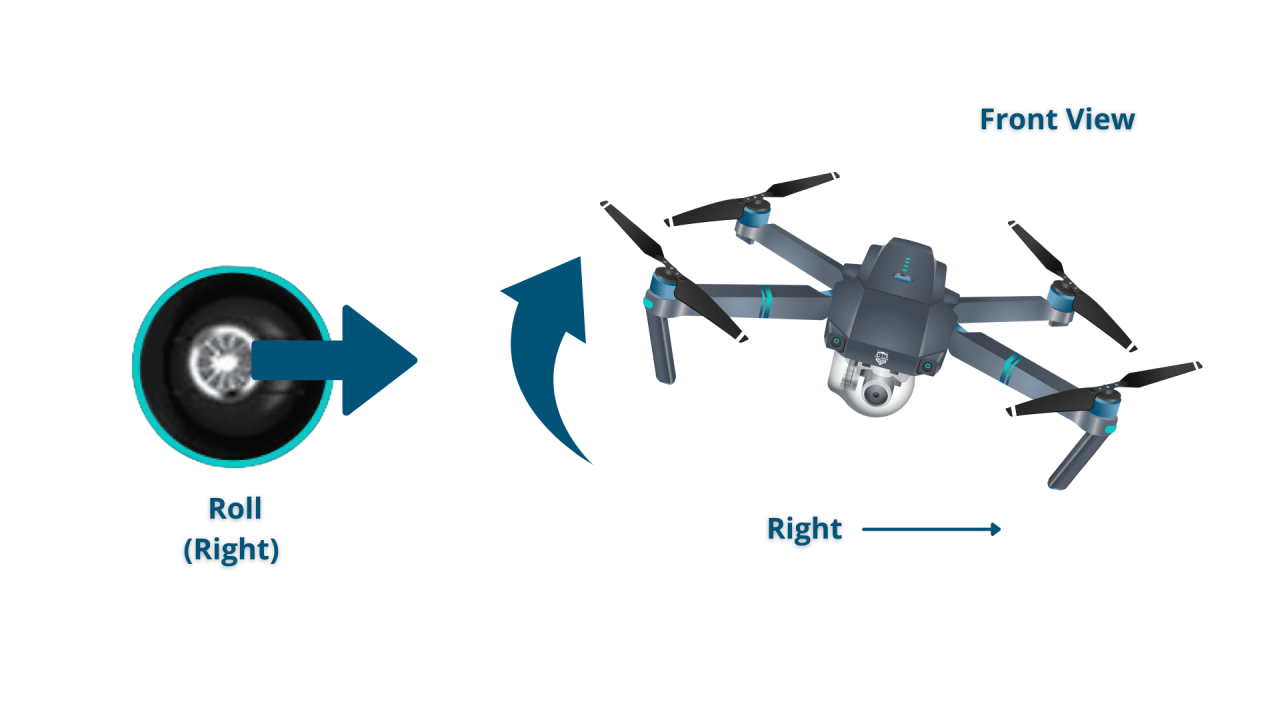
- Left Stick (Yaw/Throttle): Controls the drone’s altitude (up/down) and yaw (rotation).
- Right Stick (Pitch/Roll): Controls the drone’s pitch (forward/backward) and roll (left/right).
- Return-to-Home (RTH) Button: Initiates the automated return-to-home function.
- Emergency Stop Button: Immediately cuts power to the motors.
- Camera Control Buttons: Used to adjust camera settings (e.g., zoom, photo/video mode).
- Flight Mode Selection: Allows switching between different flight modes (e.g., GPS, Attitude).
Drone Compass and GPS Calibration
Accurate compass and GPS calibration are essential for precise drone navigation and stability. Improper calibration can lead to inaccurate positioning and erratic flight.
- Compass Calibration: With the drone powered on and placed on a level surface, rotate it slowly and steadily through a full 360-degree circle in a figure-eight pattern. Follow the instructions in your drone’s manual.
- GPS Calibration: Ensure the drone has a clear view of the sky and is in an open area away from obstructions. Allow sufficient time for the GPS to acquire enough satellites (usually indicated by a visual indicator on your controller).
Controlling Altitude, Speed, and Direction
Precise control over altitude, speed, and direction is key to smooth and controlled flights. Understanding the relationship between stick movements and drone response is crucial.
Altitude is controlled using the left stick’s vertical movement. Speed is generally controlled indirectly through the sensitivity settings and stick inputs. Direction is controlled by the combination of the right stick (pitch and roll) and the left stick (yaw). Smooth, deliberate movements are key to avoid jerky or uncontrolled flight.
Flight Modes and Features
Different flight modes offer varying levels of stability and control, making them suitable for different situations and skill levels. Understanding these modes is vital for safe and effective drone operation.
Comparison of Flight Modes
Various flight modes cater to different pilot skills and flying conditions. Selecting the appropriate mode ensures safe and efficient flight.
| Flight Mode | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPS Mode | Relies on GPS signals for position holding and stability. | Stable hovering, easy to control, good for beginners. | Requires strong GPS signal, can drift in windy conditions. |
| Attitude Mode | Maintains the drone’s orientation relative to its initial position, regardless of GPS signal. | Works without GPS, useful in GPS-denied environments. | Less stable than GPS mode, requires more skill. |
| Manual Mode | Provides full manual control over the drone’s movement. | Maximum control and responsiveness. | Requires significant skill and experience, prone to errors. |
| Sport Mode (if available) | Offers increased responsiveness and speed. | Enhanced maneuverability for experienced pilots. | Requires significant skill and precision, increased risk. |
Advanced Drone Features
Many modern drones offer advanced features enhancing safety, ease of use, and creative possibilities. These features provide additional tools for better flight management and aerial photography.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): Automatically returns the drone to its home point in case of low battery or signal loss.
- Waypoint Navigation: Allows pre-programming a flight path for autonomous flight.
- Obstacle Avoidance: Uses sensors to detect and avoid obstacles during flight.
Taking High-Quality Aerial Photos and Videos
Capturing stunning aerial footage requires understanding camera settings, composition techniques, and flight techniques. This section details how to achieve sharp, stable, and creative aerial media.
Tips for Sharp, Stable Aerial Footage
Achieving sharp and stable aerial footage involves understanding camera settings, flight techniques, and post-processing.
- Maintain a steady flight: Avoid jerky movements that can blur the footage.
- Use a gimbal (if available): A gimbal helps stabilize the camera, reducing shake and vibration.
- Adjust camera settings: Optimize shutter speed, aperture, and ISO for the lighting conditions.
- Shoot in RAW format (if possible): This provides greater flexibility in post-processing.
- Plan your shots: Visualize your composition and plan your flight path accordingly.
Impact of Camera Settings on Image Quality
Camera settings significantly influence the quality of your aerial photos and videos. Proper adjustments ensure sharp, well-exposed images.
- Shutter Speed: A faster shutter speed helps freeze motion and prevent blurring. The rule of thumb is to use a shutter speed at least twice your frame rate (e.g., 1/50th of a second for 25fps video).
- Aperture: Affects depth of field. A wider aperture (lower f-number) results in a shallower depth of field, while a narrower aperture (higher f-number) results in a deeper depth of field.
- ISO: Controls the sensitivity of the sensor to light. Lower ISO values result in cleaner images with less noise, but require more light.
Creative Composition Techniques
Effective composition enhances the visual appeal of your aerial photos and videos. Applying these techniques adds artistic flair to your work.
- Rule of thirds: Position key elements along imaginary lines dividing the frame into thirds.
- Leading lines: Use lines to guide the viewer’s eye through the image.
- Symmetry and patterns: Capture symmetrical scenes or repeating patterns for visually striking results.
- Framing: Use natural elements (e.g., trees, buildings) to frame your subject.
- Perspective: Utilize the unique perspective afforded by aerial shots to showcase your subject in a new light.
Post-Flight Procedures and Maintenance
Proper post-flight procedures and regular maintenance extend the lifespan of your drone and ensure its continued safe operation. These steps are crucial for preserving the drone’s performance and longevity.
Safe Landing and Power Down
A safe landing and power-down procedure minimizes the risk of damage to the drone and its surroundings.
- Choose a safe and level landing area.
- Slowly descend the drone to the ground.
- Once landed, power off the drone and remove the battery.
- Inspect the drone for any damage.
Drone Maintenance and Cleaning Schedule
Regular maintenance and cleaning prevent issues and prolong the lifespan of your drone. A consistent maintenance schedule is key to ensuring optimal performance.
A suggested schedule could include a visual inspection after each flight, a thorough cleaning every few flights (using a soft cloth and appropriate cleaning solutions), and more in-depth maintenance (including lubrication of moving parts) every few months or as needed.
Proper Storage of Drone and Accessories
Storing the drone and its accessories correctly protects them from damage and extends their lifespan. Appropriate storage safeguards the investment and maintains the equipment’s functionality.
Store the drone in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Batteries should be stored separately, at a moderate charge level (around 50%), and in a fire-resistant container.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding how to troubleshoot common drone problems saves time and prevents frustration. This section provides guidance on addressing frequent issues encountered during drone operation.
Identifying and Troubleshooting Common Problems
Several issues can arise during drone operation. Knowing how to address them promptly ensures a smooth flight experience.
- Low Battery: Charge the battery fully before the next flight.
- GPS Signal Loss: Relocate to an area with better GPS reception, ensure the GPS module is unobstructed.
- Motor Failure: Inspect motors for damage and replace if necessary.
- Gimbal Malfunction: Recalibrate the gimbal or check for obstructions.
- Remote Controller Issues: Check the batteries and connection.
- Propeller Damage: Replace damaged propellers.
Troubleshooting Guide (Decision Tree)
A decision tree helps guide the user through the troubleshooting process, allowing for a systematic approach to problem-solving. The tree would start with the main issue (e.g., drone won’t power on), then branch out based on possible causes, leading to potential solutions. Each branch would represent a potential cause, and the leaves would represent solutions or further diagnostic steps.
For example, if the drone won’t power on, the tree might branch into “Battery issue?” and “Power switch issue?”. Following these branches, solutions might include “Charge the battery” or “Check the power switch”.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Operating a drone responsibly involves adhering to legal regulations and ethical guidelines. Understanding these aspects ensures safe and legal drone operation.
Drone Regulations and Laws
Drone regulations vary by location and are constantly evolving. It is crucial to research and understand the specific laws in your area before flying.
Regulations often cover areas such as registration requirements, airspace restrictions, and limitations on flight time and altitude. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in fines or legal action.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations are as important as legal regulations. Responsible drone operation respects the privacy and safety of others.
- Privacy: Avoid filming or photographing people without their consent.
- Safety: Never fly recklessly or endanger others.
- Responsible Use: Use your drone for ethical and legal purposes.
Drone Operation Compliance Checklist
A checklist ensures compliance with all relevant regulations. This systematic approach minimizes the risk of violating laws or ethical guidelines.
A sample checklist might include: Checking local regulations, registering the drone (if required), obtaining necessary permissions, verifying airspace restrictions, ensuring sufficient battery power, and confirming visual line of sight. It should also include considerations for privacy and responsible flight practices.
Drone Battery Management and Safety
Lithium Polymer (LiPo) batteries require careful handling and management. Proper care ensures safe operation and extends battery life.
Proper Charging and Storage
Correct charging and storage procedures are vital for LiPo battery safety and longevity. Improper handling can lead to overheating, fire, or damage.
- Always use a designated LiPo charger.
- Never leave charging batteries unattended.
- Store batteries in a cool, dry place, away from flammable materials.
- Store batteries at a moderate charge level (around 50%).
Safety Precautions for Handling LiPo Batteries
LiPo batteries pose fire and explosion risks if mishandled. Following safety precautions is essential for safe operation.
- Never puncture or damage the battery.
- Avoid short-circuiting the battery terminals.
- Do not expose batteries to extreme temperatures.
- Dispose of damaged or swollen batteries properly.
Safe Battery Charging Station Setup
A safe charging station minimizes risks associated with LiPo batteries. This setup includes a fire-resistant surface, a designated charging area away from flammable materials, and proper ventilation to prevent overheating.
A detailed description might include a fireproof charging bag or mat placed on a non-flammable surface, such as a concrete or tile floor. The charging area should be well-ventilated, and the charger should be monitored during the charging process. A fire extinguisher should be readily available nearby.
Successfully operating a drone involves more than just understanding its controls; it demands a commitment to safety, adherence to regulations, and a continuous pursuit of skill enhancement. By diligently following the pre-flight checks, mastering the controls, and understanding the legal and ethical considerations Artikeld in this guide, you’ll be well-prepared to embark on your aerial adventures. Remember that responsible drone operation is not just about capturing stunning visuals but also about protecting yourself, others, and the environment.
Embrace the learning process, practice consistently, and always prioritize safety. Happy flying!
Answers to Common Questions
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone , which provides comprehensive guidance. Mastering these skills ensures safe and enjoyable drone operation, allowing you to explore the exciting world of aerial photography and videography responsibly.
Many user-friendly drones are available for beginners. Look for models with features like GPS stabilization, automatic return-to-home, and obstacle avoidance.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrate your drone’s compass before each flight, especially if you’re in a new location or near magnetic interference.
What should I do if I lose GPS signal during flight?
If you lose GPS signal, immediately switch to a lower altitude and carefully land the drone. Avoid flying in areas with poor GPS reception.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies depending on the model and usage. Expect flight times ranging from 15 to 30 minutes per battery charge.
What are the legal requirements for flying a drone in my area?
Drone regulations vary by location. Check with your local aviation authority for specific rules and regulations before flying.